
Aircraft fuel efficiency is crucial for both economic and environmental reasons. It helps airlines reduce costs and lowers greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a greener planet. Aviation fuel is a specialized type of petroleum-based fuel used to power aircraft. It plays a critical role in ensuring that planes can fly safely and efficiently over long distances. The most common types of aviation fuel are Jet A and Jet A-1, which are used in turbine-engine aircraft, and Avgas, which is used in piston-engine aircraft. These fuels are designed to meet fine quality and performance standards to support the demanding conditions of flight.
Jet fuel is specifically formulated to withstand extreme temperatures and provide high energy content for efficient combustion. This efficiency is crucial as it directly affects an aircraft’s fuel burn rate, which in turn impacts overall fuel efficiency and operating costs. Improvements in fuel efficiency are essential for reducing both fuel consumption and environmental impact, including CO2 emissions.
What is Aircraft Fuel Efficiency?
Fuel efficiency in aviation refers to the ability of an aircraft to maximize distance traveled per unit of fuel consumed. Factors like aircraft design, flight operations, and weather conditions play significant roles in determining fuel efficiency. Improving fuel efficiency is vital for reducing costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Aircraft fuel efficiency refers to the measure of how effectively fuel is used to perform a specific task, such as powering an aircraft over a distance. In aviation, fuel efficiency is a crucial metric that determines how much fuel is burned for each mile flown. This concept is important because it directly impacts both operational costs and environmental footprint.
Fuel efficiency improvements are essential for reducing average fuel burn, which is the amount of fuel consumed over a given distance or flight duration. Enhancements in aircraft design, such as the development of fuel-efficient engines and the use of advanced materials, play a significant role in achieving better fuel efficiency. For instance, incorporating wingtip devices can reduce drag and improve aerodynamic performance, leading to lower fuel consumption.
What is the Formula for Fuel Efficiency in Aviation?
Fuel efficiency in aviation is typically measured by how effectively an aircraft uses fuel to cover a certain distance. One of the most common formulas used to calculate fuel efficiency in aviation is the Fuel Burn per Passenger Mile. This formula helps airlines understand how much fuel is consumed for each mile traveled by each passenger. The formula can be expressed as follows:

Here’s a breakdown of each component in the formula:
- Total Fuel Burned: This is the amount of fuel consumed by the aircraft during a flight. It is usually measured in gallons or liters.
- Total Distance Flown: This is the total distance covered by the aircraft during the flight, typically measured in miles or kilometers.
- Number of Passengers: This is the total number of passengers carried on the flight.
For example, if an aircraft burns 10,000 gallons of fuel over a 2,000-mile flight with 200 passengers, the fuel efficiency would be calculated as follows:
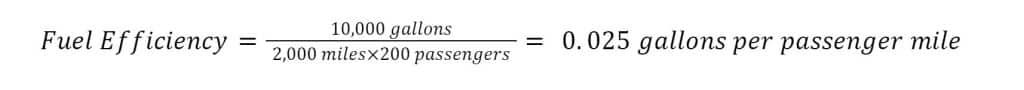
This formula gives a clear picture of how efficiently fuel is being used relative to the number of passengers and the distance traveled. It helps airlines and aviation professionals identify opportunities for efficiency improvement, such as optimizing load factor and flight operations.
Additionally, another commonly used metric is the Fuel Burn per Seat Mile. This formula is similar but focuses on the total number of seats available rather than the number of passengers:

Both formulas are valuable for assessing the fuel efficiency of aircraft, planning more efficient flights, and reducing fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. By understanding and applying these formulas, airlines can work towards achieving significant fuel efficiency gains and minimizing their environmental impact.
How Fuel Efficient Are Airplanes?
Airplanes have become increasingly fuel efficient over the years, thanks to advancements in technology and design. Modern aircraft are engineered to maximize fuel efficiency, which is crucial for reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Fuel Efficiency Improvements:
Newer aircraft models are significantly more fuel efficient than older ones. Innovations in aircraft design, such as the use of lightweight materials and aerodynamic improvements, have greatly contributed to this. For example, wingtip devices like winglets reduce drag and improve lift, leading to lower fuel consumption.
Fuel-Efficient Engines:
Advances in engine technology have also played a key role. High-bypass turbofan engines, which are common in most modern commercial jets, offer better fuel efficiency by generating more thrust with less fuel. These engines have higher compression ratios and more efficient combustion processes.
Average Fuel Burn:
The fuel efficiency of an airplane is often measured in terms of fuel burn per passenger mile. On average, modern commercial jets burn about 0.02 to 0.03 gallons of fuel per passenger mile. This means that for every mile flown, each passenger’s share of the fuel burned is roughly between 2 to 3 cents worth of fuel. This is a significant improvement compared to older aircraft, which could have a much higher fuel burn rate.
Long-Range Flights:
Long-range flights tend to be more fuel efficient per mile compared to short-haul flights. This is because a significant amount of fuel is consumed during takeoff and climb. Once the aircraft reaches cruising altitude, it can maintain a more efficient fuel burn rate. Hence, flights covering longer distances often have a lower average fuel burn per mile.
Load Factor and Seat Density:
Higher seat density and better load factors also enhance fuel efficiency. When an aircraft operates near its maximum passenger capacity, the fuel consumption per passenger decreases. This is why many cost carriers focus on maximizing the number of seats and optimizing the load factor to improve fuel efficiency.
Environmental Impact:
Improving fuel efficiency is not just about cost savings; it also has a substantial environmental impact. Fuel-efficient airplanes produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions, including CO2 emissions, which helps in the fight against climate change. The aviation industry is continuously working on reducing its carbon footprint by adopting more fuel-efficient practices and exploring alternative aviation fuels.
How to Increase Aircraft Fuel Efficiency?
Increasing aircraft fuel efficiency is a critical goal for the aviation industry, as it helps reduce operational costs and minimize environmental impact. There are several strategies and innovations that can significantly improve fuel efficiency.
1. Advanced Aircraft Design
Modern aircraft design plays a crucial role in fuel efficiency. Incorporating lightweight materials such as carbon fiber composites can reduce the aircraft’s overall weight, leading to lower fuel consumption. Improved aerodynamics, including the use of wingtip devices like winglets, reduce drag and enhance lift, resulting in more efficient flight.
2. Fuel-Efficient Engines
Developing and utilizing fuel-efficient engines is essential. High-bypass turbofan engines, for example, provide more thrust while burning less fuel. These engines are designed with advanced materials and technologies that increase efficiency and reduce average fuel burn.
3. Optimized Flight Planning
Effective flight planning is vital for reducing fuel consumption. Optimizing flight routes to take advantage of favorable winds and avoiding unnecessary detours can significantly improve fuel efficiency. Additionally, flying at optimal altitudes and speeds can reduce fuel burn.
4. Efficient Ground Operations
Reducing fuel consumption during ground operations is another important factor. Using ground power units (GPUs) instead of aircraft auxiliary power units (APUs) while on the ground can save fuel. Efficient ground handling and quick turnaround times also minimize the time engines are running idle.
5. Regular Maintenance
Keeping aircraft well-maintained ensures they operate at peak efficiency. Regular engine checks and maintenance help prevent inefficiencies caused by wear and tear. Ensuring that the airframe is free from surface roughness and other issues that increase drag is also crucial.
6. Fuel Management Techniques
Implementing effective fuel management strategies is key. This includes optimizing fuel load based on the specific requirements of each flight, balancing fuel tanks to maintain an optimal center of gravity, and using real-time fuel monitoring systems to make adjustments during flight.
7. Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs)
Using sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) can enhance fuel efficiency and reduce environmental impact. SAFs are made from renewable resources and can be blended with traditional aviation fuels to lower greenhouse gas emissions and improve overall efficiency.
8. Higher Load Factor and Seat Density
Maximizing the load factor, or the percentage of seats filled on each flight, and increasing seat density can improve fuel efficiency. By carrying more passengers per flight, airlines can distribute fuel consumption over a larger number of passengers, reducing the fuel burn per passenger mile.
9. Technological Innovations
Adopting new technologies, such as advanced avionics and flight management systems (FMS), can optimize flight paths and improve fuel efficiency. Real-time weather forecasting helps pilots adjust routes to avoid adverse conditions that can increase fuel burn.
Which Aircraft is the Most Fuel-Efficient?
Determining the most fuel-efficient aircraft involves considering various factors such as design, engine technology, and operational capabilities. Among modern commercial jets, several models stand out for their exceptional fuel efficiency due to advanced engineering and innovative technologies.
1. Airbus A350
The Airbus A350 is renowned for its fuel efficiency, largely due to its advanced aerodynamics and lightweight materials. The A350 features a carbon fiber fuselage and wings, which reduce the aircraft’s weight and improve fuel consumption. It is equipped with Rolls-Royce Trent XWB engines, which are among the most fuel-efficient engines in the industry. The A350 can achieve a significant reduction in fuel burn per seat mile, making it a favorite for long-range flights.
2. Boeing 787 Dreamliner
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner is another leading example of fuel efficiency in modern aviation. This aircraft utilizes composite materials for much of its structure, significantly reducing its weight. The 787 is powered by either the General Electric GEnx or the Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 engines, both of which offer excellent fuel efficiency. The Dreamliner also incorporates advanced aerodynamics and innovative technologies that enhance fuel efficiency, resulting in lower average fuel burn and reduced CO2 emissions.
3. Airbus A220
For regional jets, the Airbus A220 stands out as the most fuel-efficient. Originally developed by Bombardier as the CSeries, the A220 is designed with state-of-the-art aerodynamics and advanced materials. It is powered by Pratt & Whitney PW1500G geared turbofan engines, which provide superior fuel efficiency and lower greenhouse gas emissions. The A220’s fuel efficiency gains make it an attractive choice for airlines operating shorter routes.
4. Boeing 737 MAX
The Boeing 737 MAX is an upgrade of the popular 737 series, designed to be more fuel-efficient. It features CFM International LEAP-1B engines, which offer a significant improvement in fuel consumption compared to previous models. The 737 MAX also includes winglets and other aerodynamic enhancements that reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency. These improvements contribute to a lower fuel burn per passenger mile, making it an efficient option for medium-range flights.
5. Airbus A321neo
The Airbus A321neo is another highly fuel-efficient aircraft, equipped with either the Pratt & Whitney PW1100G-JM or the CFM LEAP-1A engines. These engines are designed for high efficiency and low emissions. The A321neo also features advanced aerodynamics, including sharklet wingtip devices that further enhance fuel efficiency. This aircraft is ideal for both short and medium-haul routes, offering significant fuel efficiency improvements over its predecessors.
Role of Ground Handling in Aircraft Fuel Efficiency
Ground handling plays a crucial role in enhancing aircraft fuel efficiency. Efficient ground handling operations can significantly reduce fuel consumption, lower operating costs, and minimize environmental impact. Here are several key aspects of how ground handling impacts fuel efficiency:
1- Minimizing Idle Time
Efficient ground handling reduces the time an aircraft spends on the ground with engines running. Quick turnaround procedures ensure that aircraft are prepared for the next flight as swiftly as possible. This minimizes the time engines idle on the ground, which directly reduces fuel burn.
2- Use of Ground Power Units (GPUs)
Ground Power Units (GPUs) provide electrical power to the aircraft while it is on the ground, allowing the aircraft to shut down its Auxiliary Power Unit (APU). APUs consume a significant amount of fuel, so using GPUs instead can lead to substantial fuel savings. This practice not only improves fuel efficiency but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
3- Efficient Taxi Operations
Optimizing taxi operations can greatly enhance fuel efficiency. Ground handling teams can manage taxi routes to minimize distance and delays. Additionally, single-engine taxiing, where only one engine is used during taxiing instead of two, can further reduce fuel consumption.
4- Reducing Weight
Ground handling teams are responsible for loading cargo and baggage efficiently. Proper weight distribution and efficient loading techniques help maintain optimal aircraft balance and performance. Reducing unnecessary weight, such as excess fuel or equipment, contributes to better fuel efficiency during flight.
5- Timely Maintenance and Servicing
Ground handling includes regular maintenance and servicing of aircraft systems. Ensuring that engines, tires, and aerodynamic surfaces are in top condition helps maintain fuel efficiency. For example, well-maintained engines run more efficiently, and properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance during taxiing.
6- Coordination and Communication
Effective coordination and communication between ground handling teams and flight crews are essential for efficient operations. Real-time information about weather conditions, runway status, and gate assignments allows for better planning and reduces delays, which in turn conserves fuel.
7- De-icing Procedures
In cold weather conditions, de-icing procedures are necessary for safety. Efficient de-icing operations ensure that the aircraft is ready for takeoff without unnecessary delays. This reduces the time engines are running during de-icing, saving fuel and improving overall efficiency.
8- Environmental Impact
By reducing fuel consumption through efficient ground handling, the environmental impact of aviation is also minimized. Lower fuel burn means fewer CO2 emissions and other greenhouse gases, contributing to the aviation industry’s efforts to combat climate change.
Conclusion
Enhancing aircraft fuel efficiency is essential for the future of aviation. By embracing innovations in aircraft design, adopting efficient operational strategies, and leveraging technological advancements, the industry can achieve significant fuel efficiency gains. These efforts not only reduce costs for airlines but also play a crucial role in minimizing the environmental impact of aviation. As the industry continues to evolve, prioritizing fuel efficiency will remain a key driver of sustainability and economic viability.

